Publications
Saxena Lab Members in Bold.
Jiang X*, Ly OT*, Chen H, Zhang Z, Ibarra BA, Pavel MA, Brown GE, Sridhar A, Tofovic D, Swick A, Marszalek R, Vanoye CG, Navales F, George Jr. AL, Khetani SR, Rehman J, Gao Y, Darbar D, Saxena A. Transient titin-dependent ventricular defects during development lead to adult atrial arrhythmia and impaired contractility. iScience, 27(7), 110395 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.110395
https://tinyurl.com/TitinPress
Rajan SG, Saxena A. Scents from the past: Lineage history and terminal identity in the olfactory system. Natural Sciences (Invited Highlight), e20220037 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/ntls.20220037
Ibarra BA*, Jiang X*, Treffy RW, Saxena A. Injection of human neuroblastoma cells into neural crest streams in live zebrafish embryos. STAR Protocols, 3(2), 101380 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101380
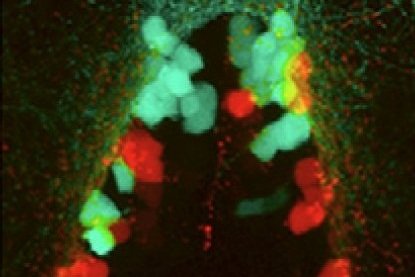
Treffy RW, Rajan SG*, Jiang X*, Nacke LM, Malkana UA, Naiche LA, Bergey DE, Santana D, Rajagopalan V, Kitajewski JK, O’Bryan JP, Saxena A. Neuroblastoma differentiation in vivo excludes cranial tumors. Developmental Cell, 56(19), 2752-2764.e6 (2021).
doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2021.09.014
https://cancer.uillinois.edu/researchers-find-location-matters-in-the-battle-against-neuroblastoma/
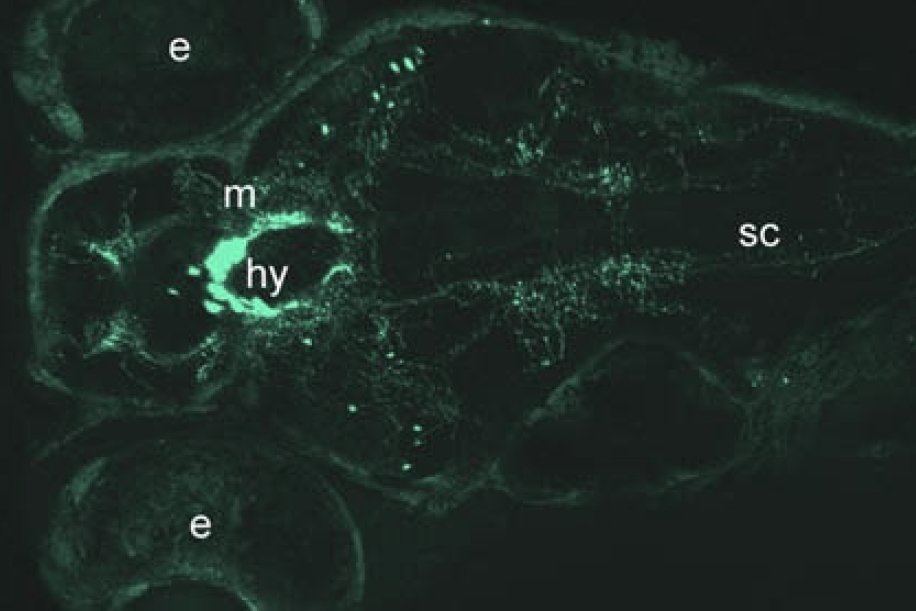
Rajan SG, Nacke L, Dhingra J, Saxena A. Notch signaling mediates olfactory multiciliated cell specification. Cells & Development (Special Issue: Quantitative Cell and Developmental Biology), Jul 2:203715 (2021).
doi.org/10.1016/j.cdev.2021.203715
Condren AR, Costa MS, Sanchez NR, Konkapaka S, Gallik KL, Saxena A, Murphy BT, Sanchez LM. Addition of insoluble fiber to isolation media allows for increased metabolite diversity of lab-cultivable microbes derived from zebrafish gut samples. Gut Microbes, 11(4), 1064-1076 (2020).
doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2020.1740073
Rajan SG, Gallik KL, Monaghan JR, Uribe RA, Bronner ME, Saxena A. Tracking neural crest cell cycle progression in vivo. genesis (Special Issue: 150 Years of Neural Crest Research), 56:e23214 (2018).
doi.org/10.1002/dvg.23214
Suarez-Bregua P, Saxena A, Bronner ME, Moran P, Rotllant, J. Targeted Pth4-expressing cell ablation impairs skeletal mineralization in zebrafish. PLOS ONE, 12(10), e0186444 (2017).
doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186444
Gallik K*, Treffy R*, Nacke L, Ahsan K, Rocha M, Green-Saxena A, Saxena A. Neural crest and cancer: Divergent travelers on similar paths. Mechanisms of Development (Special Issue: Collective Cell Migration: Biomechanics to Organogenesis; Invited Review), 148, 89-99 (2017).
doi.org/10.1016/j.mod.2017.08.002
Suarez-Bregua P, Torres-Nuñez E, Saxena A, Guerreiro P, Braasch I, Prober D, Moran P, Cerda-Reverter JM, Du SJ, Adrio F, Power DM, Canario AVM, Bronner ME, Postlethwait J, Cañestro C, Rotllant J. Pth4, an ancient parathyroid hormone lost in eutherian mammals, reveals a new brain-to-bone signaling pathway. FASEB J., 31(2), 569-83 (2017).
doi.org/10.1096/fj.201600815R
Saxena A & Bronner ME. A novel HoxB cluster protein expressed in the hindbrain and pharyngeal arches. genesis (Cover Image), 52(10), 858-63 (2014).
doi.org/10.1002/dvg.22806
Wang K, Milkie D, Saxena A, Engerer P, Misgeld T, Bronner ME, Mumm J, Betzig E. Rapid adaptive optical recovery of optimal resolution over large multicellular volumes. Nature Methods, 11(6), 625-8 (2014).
doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2925
Maier EC, Saxena A, Alsina B, Bronner ME, Whitfield TT. Sensational placodes: Neurogenesis in the otic and olfactory systems. Developmental Biology (Invited Review; Cover Image), 389(1), 50-67 (2014).
doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.01.023
Rogers CD, Saxena A, Bronner ME. Sip1 mediates an E-cadherin-to-N-cadherin switch during cranial neural crest EMT. Journal of Cell Biology (Cover Image; Highlighted), 203(5), 835-47 (2013).
doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201305050
Saxena A, Peng BN, Bronner ME. Sox10-dependent neural crest origin of olfactory microvillous neurons in zebrafish. eLife (Editor's Choice; Highlighted), 2:e00336 (2013).
doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00336
Insight: dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00648
Trinh LA, Hochgreb T, Graham M, Wu D, Ruf-Zamojski F, Jayasena CS, Saxena A, Hawk R, Gonzalez-Serricchio A, Dixson A, Chow E, Gonzales C, Leung HY, Solomon I, Bronner-Fraser M, Megason SG, Fraser SE. A versatile gene trap to visualize and interrogate the function of the vertebrate proteome. Genes & Development (Cover Image), 25(21), 2306-20 (2011).
doi.org/10.1101/gad.174037.111
Saxena A & Tabin CJ. The miRNA-processing enzyme Dicer is necessary for cardiac outflow tract alignment and chamber septation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107(1), 87-91 (2010).
doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912870107
Saxena A, Fish JE, White MD, Yu S, Smyth JWP, Shaw RM, DiMaio JM, Srivastava D. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha is cardioprotective during myocardial infarction. Circulation, 117(17), 2224-31 (2008).
doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.694992
Srivastava D, Saxena A, Dimaio JM, Bock-Marquette I. Thymosin B4 is cardioprotective after myocardial infarction. (Review) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 1112, 161-170 (2007).
doi.org/10.1196/annals.1415.048
Gao J*, Lee K*, Zhao M, Qiu J, Zhan X, Saxena A, Moore CJ, Cohen SN, Georgiou G. Differential modulation of E. coli mRNA abundance by inhibitory proteins that alter the composition of the degradosome. Molecular Microbiology, 61(2), 394-406 (2006).
doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05246.x
Bock-Marquette I*, Saxena A*, White MD, DiMaio JM, Srivastava D. Thymosin b4 activates integrin-linked kinase and promotes cardiac cell migration, survival and cardiac repair. Nature (Article; Highlighted), 432(7016), 466-72 (2004).
doi.org/10.1038/nature03000
Cowan CA*, Yokoyama N*, Saxena A, Chumley MJ, Silvany RE, Baker LA, Srivastava D, Henkemeyer M. Ephrin-B2 reverse signaling is required for axon pathfinding and cardiac valve formation but not early vascular development. Developmental Biology, 271(2), 263-71 (2004).
doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.03.026
* Equal Contribution
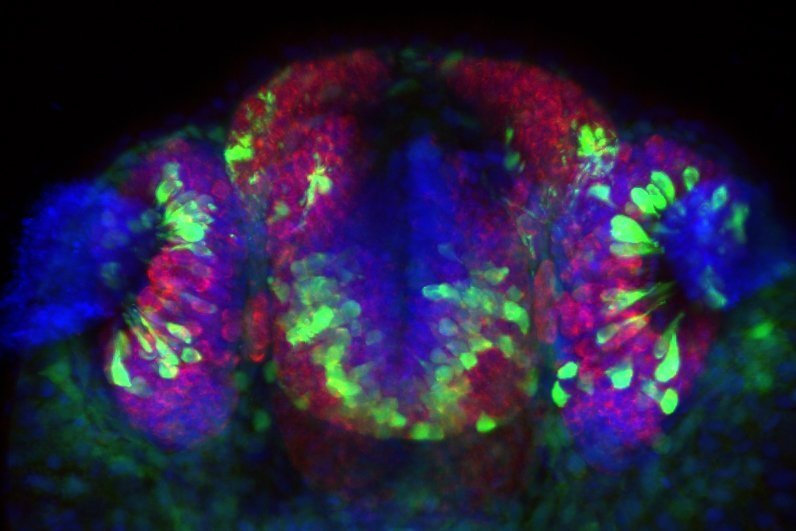
Rajan SG, Nacke LM, Lombardo JN, Manuchehrfar F, Wong K, Kanabar P, Somodji EA, Garcia J, Maienschein-Cline M, Liang J, Saxena A. Progenitor neighborhoods function as transient niches to sustain olfactory neurogenesis. Stem Cell Reports (Special Issue: Neural Stem Cells (Cover Image), 20(9), 102575 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2025.102575
https://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports/fulltext/S2213-6711(25)00242-5
https://www.uab.edu/news/research-innovation/sniffing-out-how-neurons-are-made
https://thenode.biologists.com/sniffing-out-olfactory-neurogenesis/video/
Interested in getting involved?
Learn more about joining the lab, our outreach programs, or how to donate.